- Organizations rarely have both the sufficient knowledge and resources to properly evaluate, select, and implement an enterprise application software (EAS), forcing them to turn to external partnerships.
- Inadequate and incomplete requirements skew the EAS selection in one direction or another. Many EAS projects fail due to a lack of clear description and specification of functional requirements.
- The EAS technology market is so vast that it becomes nearly impossible to know where to start or how to differentiate between vendors and products.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Accountability for EAS success is shared between IT and the business. There is no single owner of an EAS. A unified approach to building your strategy promotes an integrated roadmap so all stakeholders have clear direction on the future state.
- While technology is the key enabler of building strong customer experiences, there are many other drivers of dissatisfaction. IT must stand shoulder-to-shoulder with the business to develop a technology framework for enterprise applications.
- EAS projects are more successful when the management team understands the strategic importance and the criticality of alignment. Time needs to be spent upfront aligning business strategies with EAS capabilities. Effective alignment between IT and the business should happen daily. Alignment doesn’t just occur at the executive level but at each level of the organization.
Impact and Result
- Conduct an EAS project preparedness assessment as a means to ensure you maximize the value of your time, effort, and spending.
- Gather the necessary resources to form the team to conduct the EAS selection.
- Get the proper EAS requirement landscape by mapping out business capabilities and processes, translating into prioritized EAS requirements.
- Review SoftwareReviews’ vendor reports to shortlist vendors for your RFP process.
- Use Info-Tech’s templates and tools to gather your EAS requirements, build your RFP and evaluation scorecard, and build a foundational EAS selection framework.
Member Testimonials
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve. See our top member experiences for this blueprint and what our clients have to say.
9.2/10
Overall Impact
$85,559
Average $ Saved
23
Average Days Saved
Client
Experience
Impact
$ Saved
Days Saved
Los Angeles County Information Systems Advisory Board (ISAB)
Workshop
9/10
$408K
120
Too much reliance on COTS solutions.
PTSG Access & Safety Limited
Guided Implementation
7/10
N/A
N/A
Best - the overall process though we will be very time constrained. Less useful was the gaps in midmarket HRIS coverage apparent on the small list ... Read More
Therma Luzon, Inc.
Guided Implementation
9/10
$2,000
10
Best part on where the clarity on the business decision and alignment on the roles and responsibilities and resource that's required.
Therma Luzon, Inc.
Guided Implementation
7/10
$5,000
9
None so far. Thank you InfoTech Team! Note: The 5000 (round off from 5497) Canadian dollars is based on a costing for a solution architect on a ... Read More
Golding Contractors Pty Ltd
Guided Implementation
10/10
$5,400
2
Getting clarity around some of the tools available and some of the traps and pitfalls of the selection process
Make-A-Wish Foundation of America
Guided Implementation
9/10
$13,600
5
Confirmation of our approach and consideration for other options, vendors. Also validation the leading contender is a top player.
Town of Mooresville
Guided Implementation
10/10
$544K
120
Lower Hudson Regional Information Center
Guided Implementation
10/10
N/A
N/A
At this point I do not know what the financial and time impact will be. I'd just like to say that Hong has been an invaluable guide and support to... Read More
Methodist Ladies' College
Guided Implementation
10/10
$9,000
10
Best part is the list of requirements and use cases which we can use as a starting point.
Aquent
Guided Implementation
10/10
$136K
50
Mohegan Gaming & Entertainment
Workshop
10/10
$34,000
10
Hong and Larry did a great job facilitating and getting the team to get to the right answers. He did a great deal of work in advance to collect th... Read More
US Tax Court
Guided Implementation
9/10
N/A
7
Ricardo covered a lot of material in a short time. He was friendly, professional, efficient and also sent a fantastic follow-up E-mail with great m... Read More
Greenheck Group
Workshop
10/10
N/A
5
EA Sween Company
Guided Implementation
8/10
$1,096
4
Overall good, the templates will help standardize and the seed questions will save time on research.
The Salvation Army UK and Ireland
Guided Implementation
8/10
N/A
N/A
A first very useful session with Hong and I am looking forward to catching up with him again, once we agree internally, our next steps
Lower Hudson Regional Information Center
Guided Implementation
10/10
N/A
20
Hong Is very patient and knowledgable. He is helping to keep me focused and provides many resources to help move my project along
GENESIS CANCER CARE UK LIMITED
Guided Implementation
8/10
N/A
N/A
a lot of food for thought and ideas for next steps
Los Angeles County Development Authority
Guided Implementation
10/10
$12,330
20
very informative ! Nothing bad .
Viejas Casino
Guided Implementation
8/10
N/A
5
City of Woodbury
Guided Implementation
10/10
$2,603
5
Hong Kwok was very knowledgeable and helpful and was able to answer all of the questions I had.
University of Maribor
Guided Implementation
10/10
$14,799
5
Hong is a great communicatior, very knowledgable.
Nexus Water Group
Guided Implementation
10/10
$10,000
10
Professional draft templates and materials are so well prepared and quick to adopt and use. A real time saver and ensure a very professional proces... Read More

Application Selection & Implementation
Don’t outsource your brain: You can’t outsource project accountability to the SI.
This course makes up part of the Applications Certificate.
Please note this course is scheduled to be updated in 2026.
- Course Modules: 5
- Estimated Completion Time: 2-2.5 hours
Workshop: Select an Enterprise Application
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
Module 1: Workshop debrief – Prepare for implementation
The Purpose
- Review evaluation framework.
- Prepare for implementation.
Key Benefits Achieved
Activities
Outputs
Support the project team in establishing the evaluation framework.
- Evaluation framework considerations.
Discuss demo scripts scenarios.
- Demo script considerations.
Discuss next steps and key items in preparation for the implementation.
- RFP considerations.
Module 2: Workshop Preparation
The Purpose
The facilitator works with the team to verify organizational readiness for EAS project and form the EAS project team.
Key Benefits Achieved
- Level-set on organizational readiness for EAS
- Organizational project alignment
Activities
Outputs
Introduce the workshop and complete an overview of activities.
Complete organizational context assessment to level-set understanding.
Complete EAS readiness assessment.
- EAS readiness assessment
Form EAS selection team.
- Structured EAS selection team
Module 3: Mapping Capabilities to Prioritizing Requirements
The Purpose
- Determine the business capabilities and process impacted by the EAS.
- Determine what the business needs to get out of the EAS solution.
- Build the selection roadmap and project plan.
Key Benefits Achieved
Business and ERP solution alignment
Activities
Outputs
Map business capabilities/processes.
- Business capability/process map
Inventory application and data flow.
- List or map of application + data flow
List EAS requirements.
Prioritize EAS requirements.
- Prioritized EAS requirements
Module 4: Vendor Landscape and your RFP
The Purpose
- Understand EAS market product offerings.
- Readying key RFP aspects and expected vendor responses.
Key Benefits Achieved
- Shortlist of vendors to elicit RFP response.
- Translated EAS requirements into RFP.
Activities
Outputs
Build RFP.
- Draft of RFP template.
Build vendor response template.
- Draft of vendor response template.
Module 5: How to Evaluate Vendors
The Purpose
- Prepare for demonstration and evaluation.
- Establish evaluation criteria.
Key Benefits Achieved
Narrow your options for ERP selection to best-fit vendors.
Activities
Outputs
Run an RFP evaluation simulation.
- Draft of demo script template.
Establish evaluation criteria.
- Draft of evaluation criteria.
Customize the RFP and Demonstration and Scoring Tool.
- Draft of RFP and Demonstration and Scoring Tool.
Select an Enterprise Application
Selecting a best-fit solution requires balancing needs, cost, and vendor capability.
Analyst Perspective
A foundational EAS strategy is critical to decision-making.
Enterprise application software (EAS) is a core tool that a business leverages to accomplish its goals. An EAS that is doing its job well is invisible to the business. The challenges come when the tool is no longer invisible. It has become a source of friction in the functioning of the business.
EAS systems are expensive, their benefits are difficult to quantify, and they often suffer from poor user satisfaction. Post-implementation, technology evolves, organizational goals change, and the health of the system is not monitored. This is complicated in today’s digital landscape with multiple integration points, siloed data, and competing priorities.
Too often organizations jump into selecting replacement systems without understanding the needs of the organization. Alignment between business and IT is just one part of the overall strategy. Identifying key pain points and opportunities, assessed in the light of organizational strategy, will provide a strong foundation to the transformation of the EAS system. Learning about different vendor product offerings with a rigorous approach and evaluation framework will pave way for a better selection outcome.

Hong Kwok
Research Director
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
| Your Challenge | Common Obstacles | Info-Tech’s Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Selecting and implementing an EAS is one of the most expensive and time-consuming technology transformations an organization can undertake. EAS projects are notorious for time and budget overruns, with only a margin of the anticipated benefits being realized. Making the wrong technology selection or failing to plan for an EAS implementation has significant – and possibly career-ending – implications. |
The EAS technology market is so vast that it is nearly impossible to know where to start or how to differentiate between vendors and products. Inadequate and incomplete requirements skew the EAS selection in one direction to another. Many EAS projects fail due to a lack of clear description and specification of functional requirements. Organizations rarely have both the sufficient knowledge and resources to properly evaluate, select, and implement an EAS, forcing them to turn to external partnerships. |
EAS selection must be driven by your organization’s overall strategy. Ensure you are ready to embark on this journey with the right resources. Determine what EAS solution fits your organization through a structured requirement gathering process to a vendor evaluation framework. Ensure strong points of integration between EAS and other software such as ERP to HRIS. No EAS should live in isolation. |
Info-Tech Insight
Accountability for EAS success is shared between IT and the business. There is no single owner of an EAS. A unified approach to building your strategy promotes an integrated roadmap so all stakeholders have clear direction on the future state.
You are not just picking a piece of software, you are choosing a long-term technology partner
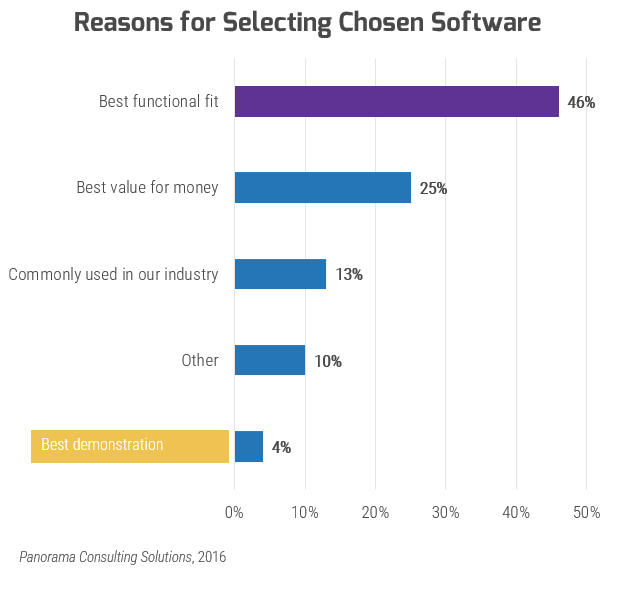
Decision making in selection often stands on functional fit; don’t forget to consider vendor fit.
As the ERP technology market becomes increasingly saturated and difficult to decode, vendors are trying to get ahead by focusing on building a partnership, not just making a sale.
68 % of organizations are satisfied with the overall ERP vendor experience, up from 54% in 2017.
Panorama Consulting Solutions, “Report,” 2018
What is an Enterprise Application?
Our Definition: Enterprise Application Software (EAS) is a large software system that provides a broad and integrated set of features which supports a range of business operations and processes across an organization. The system is broadly deployed, provides a unified interface and data structure, allowing for higher business productivity and reporting efficiencies. Best known EAS solutions include Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Human Resource Information System (HRIS), and Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
More focused EAS solutions may also bring benefits to your organization, depending on the scale of operations, complexity of operations, and functions. Here are some examples:
PSA: Professional Services Automation
SCMS: Supply Chain Management System
WMS: Warehouse Management System
EAM: Enterprise Asset Management
PIMS: Product Information Management System
MES: Manufacturing Execution System
MA: Marketing Automation
Our other Selection Framework
When selecting personal or commodity applications, or mid-tier applications with spend below $100,000, use our Rapid Application Selection Framework.

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
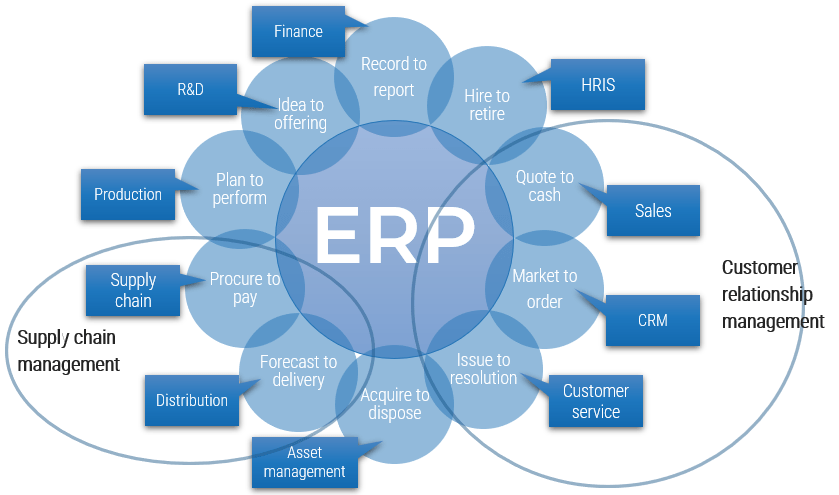
What is EPR
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems facilitate the flow of information across business units. They allow for the seamless integration of systems and create a holistic view of the enterprise to support decision making.
In many organizations, the ERP system is considered the lifeblood of the enterprise. Problems with this key operational system will have a dramatic impact on the ability of the enterprise to survive and grow.
An ERP system:
- Automates processes, reducing the amount of manual, routine work.
- Integrates with core modules, eliminating the fragmentation of systems.
- Centralizes information for reporting from multiple parts of the value chain to a single point.
| ERP use cases: | Product-centric Suitable for organizations that manufacture, assemble, distribute, or manage material goods. |
Service-centric Suitable for organizations that provide and manage field services and/or professional services. |
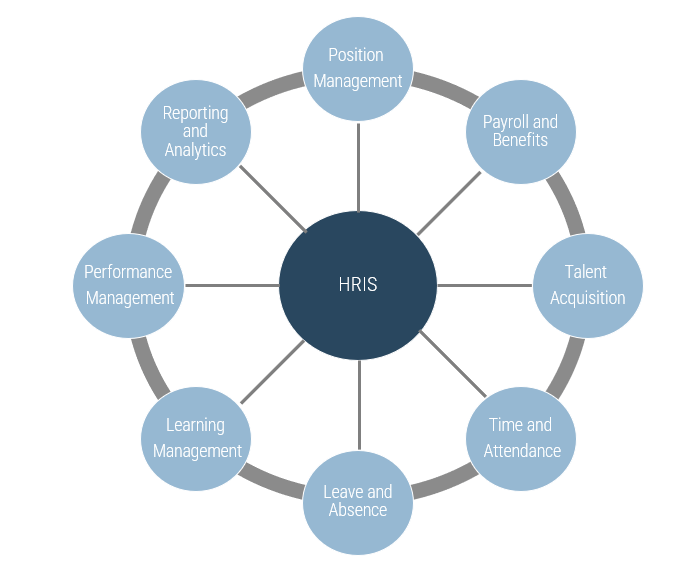
Human Resource Information System (HRIS)
What is HRIS?
An HRIS is used to acquire, store, manipulate, analyze, retrieve, and distribute information regarding an organization’s human resources. HRIS covers the entire employee lifecycle from recruit to retire.
An HRIS:
- Retains employee data in a single repository.
- Enhances employee engagement through self-service and visibility into their records.
- Enhances data security through role-based access control.
- Eliminates manual processes and enables workflow automation.
- Reduces transaction processing time and HR administrative tasks.
- Presents an end-to-end, comprehensive view of all HR processes.
- Reduces exposure to risk with compliance to rules and regulations.
- Enhances the business’s reporting capability on various aspects of human capital.
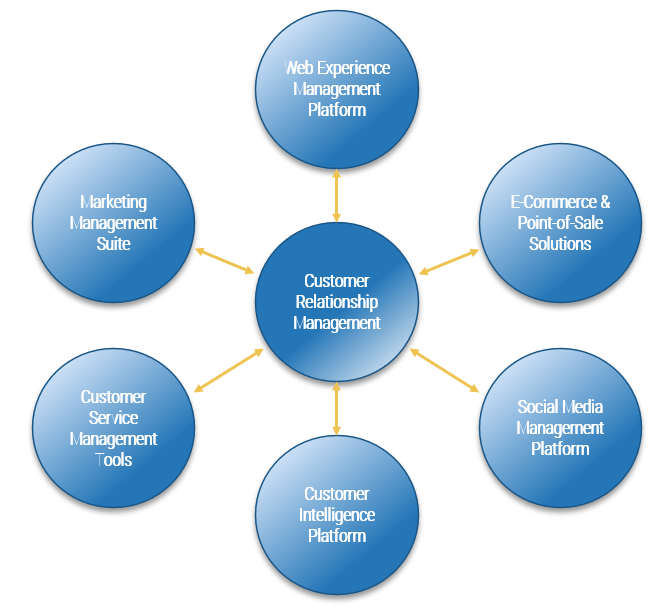
Customer relationship management (CRM)
What is CRM?
A CRM platform (or suite) is a core enterprise application that provides a broad feature set for supporting customer interaction processes, typically across marketing, sales and customer service. These suites supplant more basic applications for customer interaction management (such as the contact management module of an ERP or office productivity suite).
A CRM suite provides many key capabilities, including but not limited to:
- Account management
- Order history tracking
- Pipeline management
- Case management
- Campaign management
- Reports and analytics
- Customer journey execution
A CRM provides a host of native capabilities, but many organizations elect to tightly integrate their CRM solution with other parts of their customer experience ecosystem to provide a 360-degree view of their customers.
The good EAS numbers
There are many good reasons to support EAS implementation and use.
92% of organizations report that CRM use is important for accomplishing revenue objectives.
Source: Validity, 2020
Almost 26% of companies implement HRIS is to obtain greater functionalities, while other main reasons are to increase efficiencies, support growth, and consolidate systems.
Source: SoftwarePath, 2022
Functionality of an ERP is believed to be the most important aspect by almost 40% of companies.
Source: SelectHub, 2022
The ugly EAS numbers
Risks are high in EAS projects.
Statistical analysis of ERP projects indicates rates of failure vary from 50 to 70 percent. Taking the low end of those analyst reports, one in two ERP projects is considered a failure.
Source: Electric Journal of Information Systems Evaluation.
46% of HR technology projects exceed their planned timelines.
Source: Unleash, 2020
Almost 70% of all CRM implementation projects do not meet expected objectives.
Source: Future Computing and Informatics Journal
Enterprise Application dissatisfaction
Finance, IT, Sales, HR, and other users of the Enterprise Application system can only optimize with the full support of each other. Cooperation between departments is crucial when trying to improve the technology capabilities and customer interaction.
| Drivers of Dissatisfaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Business | Data | People and teams | Technology |
|
|
|
|
Info-Tech Insight
While technology is the key enabler of building strong customer experiences, there are many other drivers of dissatisfaction. IT must stand shoulder-to-shoulder with the business to develop a technology framework for Enterprise Applications.
Case Study
Align strategy and technology to meet consumer demand.
NETFLIX
INDUSTRY
Entertainment
SOURCE
Forbes, 2017
|
Challenge Blockbuster was the industry leader in video retail but was lagging in its response to industry, consumer, and technology trends around customer experience. |
Solution |
Results Netflix used disruptive technologies to innovatively build a customer experience that put it ahead of the long-time video rental industry leader, Blockbuster. |
Info-Tech’s methodology for selecting an Enterprise Application
| 1. Build alignment and assemble the team | 2. Define your EAS | 3. Engage, evaluate, and select | 4. Next steps | |
| Phase steps |
|
|
|
|
| Phase outcomes | Discuss organizational goals and how to advance those using the EA system. Identify gaps and remediation steps in preparation of the selection. Assemble the EA selection team. | List and review business capabilities and translate into EAS requirements. Prioritize requirements for selection. | Gain an understanding of the product offerings on the market. Engage the vendors through RFPs and conduct a proper evaluation with an objective evaluation criteria and framework. | Review and discuss the different elements required in preparation for the implementation project. |
Blueprint deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals:
ERP/HRIS/CRM Requirements Template

Accelerate your requirement gathering with a pre-compiled list of common requirements.
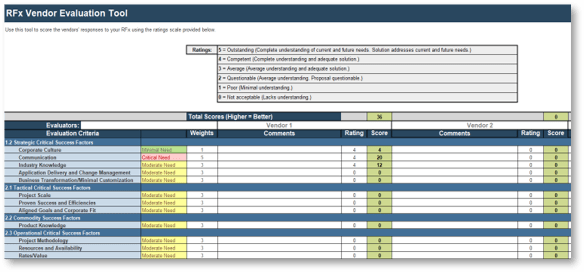
RFx Demo Scoring Tool
Quickly compare the vendors who respond to the RFx to identify the best fit for your needs.
Key deliverable:
RFx templates
Use one of our templates to build a ready-for-distribution implementation partner RFx tailored to the unique success factors of your implementation.
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
| DIY Toolkit | Guided Implementation | Workshop | Consulting |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful." | "Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track." | "We need to his the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place." | "Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project." |
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks are used throughout all four options
Guided Implementation
A Guided Implementation (GI) is a series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization.
A typical GI is between six to ten calls over the course of four to six months.
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?
| Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Phase 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Call #1: Scoping call to understand the current situation. Call #2: Discuss readiness and resourcing needs. |
Call #3: Discuss the capabilities and application inventory. Call #4: Discuss requirement gathering and prioritization. |
Call #5: Go over SoftwareReviews and review draft RFx. Call #6: Discuss evaluation tool and evaluation process. |
Call #7: Discuss preparation for implementation. |
Workshop Overview
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activities |
Organizational Strategic Needs 1.1 Review the business context. 1.2 Overview of the EAS Landscape 1.2 Assess EAS project readiness 1.3 Determine the members of the EAS selection team |
From Capabilities to Requirements 2.1 Map business capabilities 2.2 Inventory application and interactions 2.3 Gather requirements 2.4 Prioritize requirements |
Vendor Landscape and Your RFP 3.1 Understanding product offerings 3.2 Build a list of targeted vendors 3.3 Build RFP 3.4 Build vendor response template |
How to Evaluate Vendors 4.1 Run a RFP evaluation simulation 4.2 Build demo script 4.3 Establish evaluation criteria |
Next Steps and Wrap-Up (offsite) 5.1 Clean up in-progress deliverables from previous four days. 5.2 Set up review time for workshop deliverables and to discuss next steps. |
| Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
|
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889

 Build Your Enterprise Application Implementation Playbook
Build Your Enterprise Application Implementation Playbook
 Master Contract Review and Negotiation for Software Agreements
Master Contract Review and Negotiation for Software Agreements
 Negotiate SaaS Agreements That Are Built to Last
Negotiate SaaS Agreements That Are Built to Last
 Governance and Management of Enterprise Software Implementation
Governance and Management of Enterprise Software Implementation
 Select Software With the Right Satisfaction Drivers in Mind
Select Software With the Right Satisfaction Drivers in Mind
 Select an Enterprise Application
Select an Enterprise Application
 Optimize Your Software Selection Process: Why 5 and 30 Are the Magic Numbers
Optimize Your Software Selection Process: Why 5 and 30 Are the Magic Numbers
 The Rapid Application Selection Framework
The Rapid Application Selection Framework
 Get the Best Discount Possible With a Data-Driven Negotiation Approach
Get the Best Discount Possible With a Data-Driven Negotiation Approach
 Craft a Customer-Driven Market Strategy With Unbiased Data
Craft a Customer-Driven Market Strategy With Unbiased Data
 Switching Software Vendors Overwhelmingly Drives Increased Satisfaction
Switching Software Vendors Overwhelmingly Drives Increased Satisfaction
 Make the Case for Legacy Application Modernization
Make the Case for Legacy Application Modernization
 Empower Solution Delivery With the Right CoP, CoE, and C4E Model
Empower Solution Delivery With the Right CoP, CoE, and C4E Model
 Enterprise Application Change: It's All About Business Capabilities
Enterprise Application Change: It's All About Business Capabilities
 2020 Applications Priorities Report
2020 Applications Priorities Report
 AI-Assisted Code Generation Tools
AI-Assisted Code Generation Tools