- Organizations need to undergo fast and effective changes to remain relevant.
- Changes are occurring with increased frequency.
- There’s a high dependence on IT to succeed at these changes.
- Yet, changes are still more likely to be unsuccessful than successful.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Organizational Change Management is not about creating a “Communications Plan” just before go-live. It is about making sure every change delivers value by driving user adoption and ensuring solutions are appropriate and understood.
- One size does not fit all. Managing organizational change does not mean adopting every recommendation from best-practice OCM frameworks. Build your OCM canvas with activities that suit your change and organization.
- OCM should go back to the origin of the idea and support and engage people throughout the process, rather than last minute OCM approaches or starting OCM only when encountering resistance. Doing the right thing at the right time is critical for success.
Impact and Result
Successfully adopting and sustaining changes, and realizing the intended benefits through:
- Ensuring that OCM is actively considered from beginning to end, from assessing impacts and empathizing with impacted groups to understand their needs all the way to making change “normal practice”.
- Breaking changes into digestible components to make it manageable. Organizational Change Management does not need to be complex. Setting short term goals will help the change process go smoothly and achieve success.
- Planning for the unexpected. Working with people brings different challenges that must be addressed, consider the emotional, behavioral, and cultural factors that foster resistance and inhibit adoption.
- Taking the time upfront to be planful about a sustainment strategy and refining it accordingly along the way to prevent resorting to old behaviors.
Workshop: Drive Adoption and Sustain Transformational Change
Workshops offer an easy way to accelerate your project. If you are unable to do the project yourself, and a Guided Implementation isn't enough, we offer low-cost delivery of our project workshops. We take you through every phase of your project and ensure that you have a roadmap in place to complete your project successfully.
Module 1: Answer “Why and What?”
The Purpose
Assess the organization’s OCM maturity and the drivers forcing the organization to change.
Key Benefits Achieved
- Understand organization’s current strengths and weaknesses regarding OCM, the purpose of the chosen change, and develop a compelling future-state vision.
Activities
Outputs
Assess the current OCM maturity.
- Cultural readiness and process maturity results
Define the change pilot.
Identify change drivers, value sources, and create a purpose statement.
- Purpose statement
Create a change vision statement.
- Vision statement
Module 2: Prepare and plan the change
The Purpose
Assess impacts, risks, analyze impacted groups to identify the required change team and break change into critical change moments.
Key Benefits Achieved
- Clear understanding of impacts, risks, and impacted groups’ needs.
- Defined change team, roles, and responsibilities.
- Overall change broken into digestible critical change moments with identified metrics.
Activities
Outputs
Assess organizational change impact.
- Identified impacts and risks
- Risk score and rating
Analyze impacted groups/individuals.
- Impacted groups/individuals map
- Impacted groups/individuals network
Define the change team and roles.
- Identified change team and RACI matrix
Break change vision into critical change moments.
- Critical change moments, owners, targeted dates, dependencies, success criteria and celebrations
Identify success metrics.
- Defined success metrics
Module 3: What to expect during the change process
The Purpose
Create tailored communications, training, resistance management and feedback gathering plans.
Key Benefits Achieved
Tailored plans to fulfill impacted groups/individuals needs rather than leaders’ guesses.
Activities
Outputs
Create a communications plan.
- Communications plan
Identify gaps and plan for required training.
- Training plan
Define resistance management tactics.
Define feedback gathering and evaluation methods.
- Feedback gathering plan
Module 4: Achieve and sustain the intended value
The Purpose
Plan upfront a sustainment strategy.
Key Benefits Achieved
Clearly identified required sustainment components and plans to implement them.
Activities
Outputs
Identify the required sustainment components.
- Sustainment plan
Plan for post-project sustainment, and benefits realization accountabilities.
- Accountabilities and RACI matrix for benefits realization after the project is closed
Drive Adoption and Sustain Transformational Change
Analyst perspective
The pace of change has never been faster, and the urgency to embrace change has never been more crucial.
While the speed, frequency, and interdependence of changes increase, so too does the rate of change failure. The missing piece of the puzzle is about people: their expectations, emotions, behaviors, culture, habits, beliefs, and resistance. Technological evolution continues to accelerate, but the on-time, on-budget execution of projects won't drive value if customers and users are not willing, able, or committed to adopting these projects' outcomes.
Addressing the people side of the change equation will look different for every organization and will probably be different for various groups within the same organization. Effective organizational change management (OCM) is not about adopting every best practice found; instead, it's about assessing and right-sizing OCM efforts according to people's needs.
Investing in supporting people during change should be as important as investing in the latest technologies – only then will we be able to realize and sustain the value we want and expect.

Laura Herran Sanchez
Research Specialist, Special Projects
Info-Tech Research Group
Drive Adoption and Value From Organizational Change
Champion OCM and leave nothing behind.
EXECUTIVE BRIEF
Executive summary
Your challenge
The next generation of technologies requires:
- Acknowledgement from organizations that they need to undergo fast and effective change to remain relevant.
- An ability to sustainably accelerate to keep pace with the increased frequency of change.
- Confidence in IT to reliably execute these changes.
- Unfortunately, change efforts remain more likely to be unsuccessful than successful.
Common obstacles
Some of the major factors preventing organizations from achieving value from new technologies include the following:
- Projects are staffed but change management is not, resulting in limited accountability for solution adoption and value realization.
- Change management activities are introduced too late, the impact of the change is not fully understood, and negative effects are not mitigated.
- Value delivery is delayed, which can lead to intended outcomes getting lost and even defunding.
Info-Tech's approach
Effective organizational change management (OCM) can help you achieve and sustain intended value and benefits by:
- Ensuring that OCM is actively considered from the beginning through to the end of a project.
- Breaking change up into digestible components to make it manageable.
- Planning for the unexpected.
- Taking the time upfront to be planful about a sustainment strategy.
Info-Tech Insight
OCM is not about creating a communications plan just before go-live. It's about making sure every change delivers value by driving user adoption and ensuring solutions are appropriate and understood.
Your challenge
All IT leaders and organizations are at risk of falling behind if they do not embrace emerging technologies fast enough.
- Today's landscape is constantly evolving, making it necessary for organizations to adopt organizational changes faster and more frequently.
- Transformation efforts require enormous financial investments and time, but the return on that investment is rarely defined and realized.
- Organizational strategies are often driven and enabled through technologies, resulting in a high dependence on IT to ensure success.
- IT leaders and organizations must cope with various change initiatives happening simultaneously that vie for the same resources.
- Completed projects aren't necessarily successful projects. Most fall short of stated objectives and expected value is often not achieved or sustained long term.
- Failing to achieve the desired results can erode IT's relationship with other parts of the organization.
85% of organizations agree that embracing new technologies will drive transformation in their organization.
Source: World Economic Forum, 2023
"51% of technology executives have not seen an increase in performance or profitability from digital transformation investments."
Source: KPMG, 2023
Common obstacles
The following obstacles make technology adoption and value realization difficult to achieve for many organizations:
IT leaders and business leaders are not aligned before, during, or after transformation initiatives.
Transformation and change are terms often used interchangeably, resulting in the false belief that both are happening when they're not.
People believe that they can transform the organization simply by implementing technologies, deprioritizing or overlooking the critical human aspects.
Organizational change is perceived as a project with an end date instead of as an ongoing practice, so it is rarely sustained, and the anticipated post-project value is not realized.
Last-minute approaches to OCM are always ineffective and inauthentic.
While stated belief in OCM concepts is virtually ubiquitous, the reality is that the adoption of OCM practices is near zero.
One reason for high failure rates is that most leaders focus on the processes – the hard skills and tools needed to create the desired result – and they underestimate the challenges related to the people.
– David A. Shore, Faculty, Harvard University
47% of employees believe alignment issues have been preventing projects from meeting objectives.
Source: Lucid, 2023
Info-Tech's approach
By implementing effective OCM, your organization can drive adoption and value.
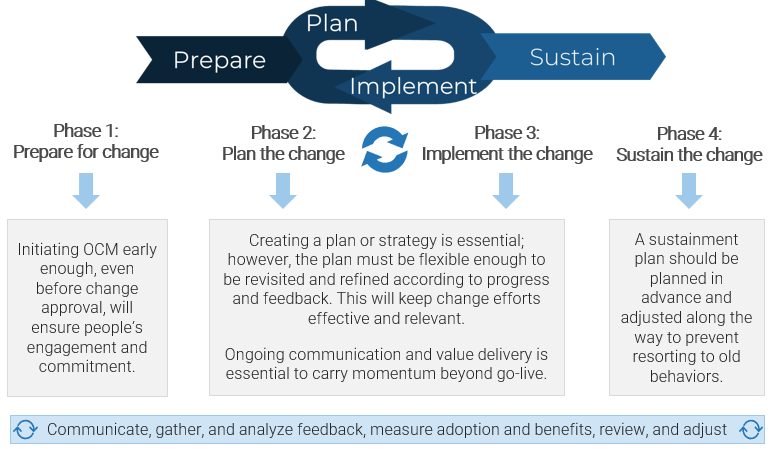
The Info-Tech difference:
- OCM starts at the point of idea origin and supports people throughout the process to ensure engagement and commitment.
- Take the time upfront to be planful about your change and sustainment strategy.
- Assess readiness and all vested interests to create a customized, relevant, and detailed action plan to effectively address change.
- Consider the emotional, behavioral, and cultural factors that foster resistance and inhibit adoption.
- Break change up into digestible components to make it manageable.

Organizational change is not just beneficial – it's crucial
Changes are happening faster and more frequently. Inability to actively adopt change will lead organizations to failure.
- Dealing with sudden changes and unexpected disruption is the new norm. Organizations need to be able to pivot and quickly adapt if they want to survive.
- 56% of senior executives that have seen an increase in the number of change projects have seen an increase greater than 25%, while an additional 25% have seen an increase greater than 50% (Harvard Business Review, 2023).
- Changes are not only driven by crisis but also by emerging technologies, changing needs or expectations of interest groups, fierce competition, anticipated opportunities, and other internal and external forces.
- Organizations in the modern world need to do more than react to change drivers. They should actively anticipate and embrace them to stay relevant and generate value.
85% of senior executives have seen an increase in the number of change projects.
Source: Harvard Business Review, 2023
85% of CIOs believe their role is shifting
to that of a changemaker.
Source: Foundry, 2023
With the rapid increase of change, OCM can no longer be overlooked or misunderstood
- OCM addresses the people side of change.
- OCM manages change that requires replanning and reorganizing of things people are already doing, causing them to feel like they have lost control over aspects of their jobs (Journal of Organizational Change Management, 2017).
- OCM is a framework for managing the introduction of new processes and technologies to ensure adoption by those affected.
- OCM can help improve outcomes on any project where you need people to adopt new tools and procedures, comply with new policies, learn new skills and behaviors, or understand and support new processes.
- OCM involves tools, templates, and processes to help project leaders analyze the impacts of a change, engage impacted groups/individuals, and train users on new technologies and processes.
- OCM is a separate body of knowledge, but as a practice it is inseparable from both project management and business analysis.

 Drive Adoption and Sustain Transformational Change
Drive Adoption and Sustain Transformational Change
 Build an Annual IT Talent Strategy
Build an Annual IT Talent Strategy
 Lead Staff through Change
Lead Staff through Change
 Build an IT Succession Plan
Build an IT Succession Plan
 Mitigate Key IT Employee Knowledge Loss
Mitigate Key IT Employee Knowledge Loss
 2020 IT Talent Trend Report
2020 IT Talent Trend Report
 Pandemic Preparation – The People Playbook
Pandemic Preparation – The People Playbook
 The Complete Manual for Layoffs
The Complete Manual for Layoffs
 Streamline Your Workforce During a Pandemic
Streamline Your Workforce During a Pandemic
 2021 IT Talent Trend Report
2021 IT Talent Trend Report
 IT Diversity & Inclusion Tactics
IT Diversity & Inclusion Tactics
 Design and Sustain a Purposeful IT Culture
Design and Sustain a Purposeful IT Culture
 The Accessibility Business Case for IT
The Accessibility Business Case for IT
 Communicate Any IT Initiative
Communicate Any IT Initiative
 Effective IT Communications
Effective IT Communications
 Initiate Digital Accessibility for IT
Initiate Digital Accessibility for IT
 Improve IT Team Effectiveness
Improve IT Team Effectiveness
 Build a Regular CEO IT Update Package
Build a Regular CEO IT Update Package
 CIO Time Study
CIO Time Study
 IT Talent Trends 2024
IT Talent Trends 2024
 Crack the Code to Successful Transformation Management
Crack the Code to Successful Transformation Management
 Chart Your Path: From Enterprise Architect to the Next CIO
Chart Your Path: From Enterprise Architect to the Next CIO
 Reputation Equals Revenue: Why Reputation Matters to IT as a Professional Service
Reputation Equals Revenue: Why Reputation Matters to IT as a Professional Service
 Strengthening the CIO Brand: From Perception to Reality
Strengthening the CIO Brand: From Perception to Reality
 Adaptive IT Leadership
Adaptive IT Leadership
 IT Talent Trends 2025
IT Talent Trends 2025
 Adaptive IT Leadership Keynote
Adaptive IT Leadership Keynote
 Leading People Change in the Face of Disruptive Technology
Leading People Change in the Face of Disruptive Technology
 The Race to Develop Talent
The Race to Develop Talent