- Increasing regulations require significant investments in compliance and operational adjustments.
- Continuing disruptions to supply chains are forcing manufacturers to rethink sourcing strategies.
- Changing consumer expectations are pushing manufacturers to innovate, adapt, and stay competitive.
- Inflation, energy prices, and labor shortages are driving up costs and squeezing margins.
- Competitors are rapidly investing in technology, resulting in increasing competition in the marketplace.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
CIOs will have to serve as strategic enablers who can help align technology with business objectives, enhance operational resilience, and position manufacturers for sustained success in an increasingly digital and competitive market landscape.
Impact and Result
- A comprehensive look at prevailing trends and their impact on current operating conditions.
- Pointers and case studies on how manufacturers can capitalize on these trends and transform them into business opportunities.
The Future of Non-Durable Goods Manufacturing
trends shaping future business opportunities
Analyst Perspective
The non-durable goods manufacturing industry is facing a host of global challenges, driven by new regulations, evolving consumer behaviors, geopolitical instability, and economic pressures:
- Strict regulations are requiring manufacturers to rethink their production processes and supply chain strategies.
- Changing consumer preferences are pushing companies to innovate and adapt rapidly.
- Geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and rising tariffs have disrupted global supply chains, making it harder for manufacturers to source raw materials and distribute products efficiently.
- Inflationary pressures and fluctuating energy costs are further straining operational budgets.
Manufacturers are adopting a range of strategies to stay competitive and resilient. Many are investing in digital transformation initiatives, leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and the internet of things (IoT) to improve efficiency, optimize production, and reduce waste. Supply chain diversification has become a top priority, with companies exploring nearshoring, multisourcing, and increased inventory buffers. Sustainability initiatives are also being accelerated, with manufacturers adopting greener practices to align with regulatory requirements and meet consumer expectations. Data is helping businesses by providing actionable insights into demand forecasting, pricing strategies, and inventory management.
To achieve long-term success, manufacturers must invest in workforce development through upskilling and reskilling programs, embrace smart manufacturing technologies to enhance productivity, offer personalized products that align with evolving consumer values, and strengthen partnerships across the supply chain. These strategies will help them navigate uncertainties and position themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly complex global landscape.

Shreyas Shukla
Principal Research Director, Manufacturing Industry
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
Increasing regulations require significant investments in compliance and operational adjustments.
Continuing disruptions to supply chains are forcing manufacturers to rethink sourcing strategies.
Changing consumer expectations are pushing manufacturers to innovate and adapt to stay competitive.
Inflation, energy prices, and labor shortages are driving up costs and squeezing margins.
Competitors are rapidly investing in technology, resulting in increasing competition in the marketplace.
Common Obstacles
Rising operational costs are making it challenging for manufacturers to invest in growth initiatives.
Lack of skilled labor hinders the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies.
Outdated systems and a lack of integration between IT and operational technology (OT) slow down innovation and efficiency improvements.
Supply chain vulnerabilities, geopolitical instability, and evolving policies lead to supply chain disruption and higher production costs.
Competition is continuously increasing from local and global players, thus diluting profitability.
Info-Tech’s Approach
Info-Tech recognizes the role of CIOs in driving the growth and profitability agenda for manufacturers. This research aims to empower CIOs with the knowledge they need to build a forward-facing transformation strategy that includes the right mix of enablers and differentiators, so their organization can be positioned for growth.
Info-Tech will provide:
- A comprehensive look at prevailing trends and their impact on current operating conditions.
- Pointers and case studies showing how manufacturers can capitalize on these trends to transform them into business opportunities.
Info-Tech Insight
CIOs have to serve as strategic enablers who can help align technology with business objectives and enhance operational resilience, thus positioning manufacturers for sustained success in an increasingly digital and competitive market landscape.
Global supply chains are set to face their biggest challenge since the COVID-19 pandemic
Rising tariffs, weak economies, and escalating geopolitical tensions threaten the stability of global supply chains and trade. The unique tariff diplomacy approach launched recently by the US, causing cascading retaliatory measures from some of its largest trading partners, will reset international trade relations for years to come. Added to this, weakening economies in the EU and Canada, as well as ongoing conflicts, have resulted in mounting costs, delays, and uncertainty in sourcing for manufacturers.
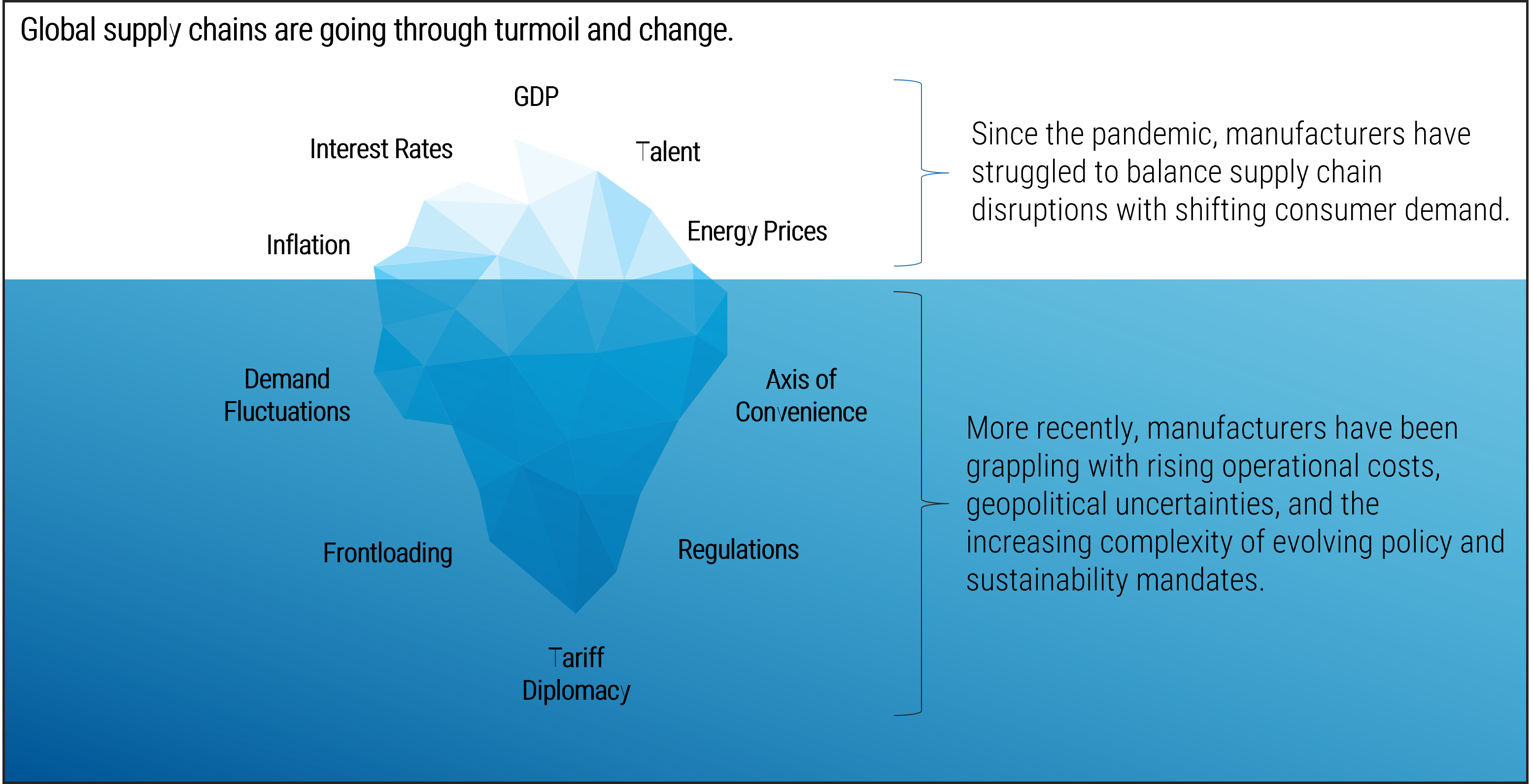
The US has launched a global trade war.
“Trump’s tariffs on his northern and southern neighbors would disrupt almost US$1.5 trillion in trade... A Sino-US trade war, affecting bilateral trade of about US$600 billion may be even harder to manage for the at least 612 US domiciled companies with facilities in China.” (Source: Mapping the impact of tariffs on supply chains, Bloomberg, 2025)
A complex macroeconomic landscape is disrupting manufacturers and their supply chains
Manufacturers are being forced to deal with complex global forces. While some key macroeconomic metrics indicate the ability to invest in expansion and new technologies, other metrics are likely to impact purchasing power, consumer sentiment, and the availability of talent and cheap energy. Manufacturers will have to balance their investment decisions carefully.
Inflation is returning to normal levels.
Average reduction of 1.5% globally
- Global inflation is projected to fall from 5.8% in 2024 to 4.3% in 2025, after peaking at 9.4% in 2022. However, inflation will likely increase due to rising tariffs.
- A reduction in global inflation positively impacts manufacturers by lowering input costs for raw materials, energy, and transportation, leading to improved profit margins.
Interest rate reduction will stimulate growth.
Average reduction of 1.5-2% globally
- The central banks of Canada, the US, the UK, Europe, and China started cutting interest rates in 2024 as inflation came under control. Cuts might be accelerated in response to increasing inflation from tariffs.
- This benefits the sector by lowering borrowing costs, enabling companies to invest in new technologies, capacity expansion, and operational improvements.
GDP will be slow to grow.
Global growth rate of 3.2%
- Global GDP is expected to remain at 3.2% in 2024 and 2025. The economies of the US, China, and India are expected to grow at a slower pace while the economies of the UK and Europe are expected to perform better.
- This will negatively impact demand, resulting in lower production volume and a decline in revenue, which will delay expansion and cost-intensive projects.
Employment is generally stable.
No expected change in global unemployment rate
- Unemployment rates in the US and Australia are expected to increase marginally, while the UK, Europe, China, and India are seeing small reductions.
- Reducing unemployment rates contribute to higher purchasing power. AI and automation continue to cause long-term concerns as manufacturers are having to step up hiring and training investments.
Energy prices continue to fluctuate.
Average decrease of 8% globally
- Global oil prices have remained largely stable, with minor reductions expected in 2025.
- However, escalation of geopolitical conflicts and voluntary oil production cuts by OPEC can have a significant impact on the price of oil very quickly. This will require a shift toward efficient technologies and renewable sources.
(Source: GEP, 2025)
The US has imposed tariffs on some of its closest trading partners, risking a trade war
The potential of US-imposed tariffs has escalated tensions and triggered retaliatory measures. This trade war has the potential to disrupt global supply chains, increase costs for manufacturers, and lead to price volatility in key industries. As nations impose counter-tariffs, businesses will face rising production costs and shifting trade routes, impacting economic growth worldwide. The uncertainty surrounding trade policies is forcing companies to reassess sourcing strategies and explore alternative markets.
Tariff Diplomacy
There could be a US$1.1 trillion tax increase over the next decade. (Source: Tax Foundation, 2025)
- Proposed US tariffs on Mexico, Canada, and China (effective February 2025) would shrink GDP by 0.4%, increase taxes by $1.1 trillion, and cost $800 per US household in 2025 alone.
- If permanently imposed, these tariffs could trigger 330,000+ job losses and increase costs for businesses and consumers.
Demand Fluctuations
Taxes increased US$800 per US household in 2025. (Source: Tax Foundation, 2025)
- Previous tariffs have led to an annual tax increase of $625 per US household, with 2025 tariffs adding another $800 per household, reducing demand for goods.
- Tariffs on Mexico, Canada, and China are projected to shrink US GDP by 0.4%, forcing businesses to cut investments and reduce hiring.
Frontloading
Trans-Pacific container volumes are expected to contract by 10% in 2025. (Source: McCarthy Tetrault, 2025)
- Major companies proactively accelerated imports to avoid tariff costs.
- Some businesses acted months in advance. This led to higher storage costs and logistical bottlenecks that will continue well into the future, showing how disruptive tariffs are to supply chains.
Regulations
US$3 trillion is the cost of regulations to US economy. (Source: “The Cost of Federal Regulations,” NAM, 2024)
- Manufacturers face over 200,000 federal restrictions, making compliance costly and limiting growth.
- Small manufacturers, which make up 90% of the sector, struggle with borrowing due to financial regulations.
- Tax reforms and effective policies could boost investment and attract foreign manufacturers.
Axis of Convenience
US$2 billion of manufactured goods cross North American borders daily. (Source: “Six things that could get more expensive for Americans under Trump tariffs,” BBC, 2025)
- Companies are shifting production to countries with favorable trade agreements in order to bypass tariffs, forming an "axis of convenience.”
- Businesses are investing in nearshoring and friendshoring, relocating supply chains to allied nations to reduce reliance on volatile markets and ensure tariff-free access.
Business enablers and differentiators empower manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market dynamics
Focusing on business enablers and differentiators allows manufacturers to adapt to technological advancements, shifting consumer demands, and competitive pressures. Business enablers provide manufacturers with the foundational capabilities needed to drive innovation, efficiency, and resilience in an evolving market landscape. Differentiators, on the other hand, help manufacturers stand out by offering unique value propositions, enhancing customer experiences and achieving sustainable growth.
Embrace the relevant enablers and differentiators to position your organization competitively.
Enablers
- AI use improves efficiency and decision-making.
- Data use improves forecasting and production.
- Supply chain digitization enables agility and resilience.
Differentiators
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) use improves monitoring and reduces downtime.
- Sustainability efforts cut waste and emissions.
- Talent development drives innovation and productivity.
Info-Tech Insight
AI is transforming manufacturing.
The changes that come will not only reshape how manufacturers operate but also how they deliver value.
Organizations that embrace this shift and invest in the right tools, data infrastructure, and talent will be positioned to unlock value and outpace their competitors.
Leveraging the right business enablers allows manufacturers to remain agile, seize new opportunities, and navigate uncertainties
Business enablers encompass a wide range of elements, including advanced technologies, process improvements, and strategic frameworks, that collectively enhance efficiency, agility, and resilience. By integrating automation, data analytics, cloud computing, smart manufacturing practices, and supply chain transparency, manufacturers can streamline their operations, optimize supply chains, and enhance product quality while keeping costs low.
Business enablers provide the essential tools, technologies, and strategies so manufacturers can remain competitive.
AI
- AI serves as a powerful business enabler by automating complex processes, enhancing decision-making with data-driven insights, and driving innovation across operations.
- AI helps optimize production, improve quality control, and personalize customer experiences while reducing costs and inefficiencies.
- By leveraging AI, businesses can achieve greater agility, resilience, and competitiveness.
Data
- Data acts as a crucial business enabler by providing actionable insights that drive informed decision-making.
- Data helps manufacturers identify trends, predict demand, and improve product quality through real-time monitoring and analytics.
- Leveraging data effectively enables businesses to stay agile, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge.
Supply Chain
- A resilient supply chain serves as a key business enabler by ensuring the seamless flow of materials, reducing disruptions, and maintaining operational continuity.
- It also helps manufacturers adapt to market fluctuations, meet customer demands efficiently, and optimize costs through strategic sourcing and logistics.
- By building resilience, businesses can enhance agility, mitigate risks, and sustain long-term growth.
Manufacturers are seeing a positive return on investment (ROI) from AI use.
64% of manufacturing firms report seeing positive ROI from Gen AI use cases in production. (Source: Dataiku and Databricks, 2024)
Leveraging the right differentiators provides a competitive edge and addresses evolving consumer expectations and regulatory requirements
Differentiators play a crucial role in helping manufacturers establish a unique market position, outperform competitors, and drive long-term success in an increasingly crowded and dynamic industry. They represent the distinct attributes, capabilities, and value propositions that set a business apart from others, enabling it to attract and retain customers while fostering brand loyalty and market leadership.
Differentiators allow manufacturers to offer unique value, build strong customer relationships, and remain agile in the face of change.
Operations Technology
- Advanced operations technology (OT) and its convergence with IT enable seamless integration of production processes with enterprise systems.
- This convergence enhances real-time data visibility, predictive analytics, and automation, driving smarter decision-making and operational excellence.
- By bridging OT and IT, manufacturers can achieve greater flexibility, resilience, and competitive advantage in an increasingly digital landscape.
Sustainability
- Sustainability and the use of green energy act as key differentiators by reducing environmental impact, enhancing regulatory compliance, and appealing to eco-conscious consumers and stakeholders.
- By adopting renewable energy sources and sustainable practices, manufacturers can improve brand reputation and drive long-term resilience.
- Embracing sustainability provides a competitive edge in an increasingly eco-driven market.
Talent
- A highly trained workforce serves as a critical differentiator by driving innovation, operational efficiency, and adaptability in an evolving manufacturing landscape.
- Skilled employees enable manufacturers to leverage advanced technologies, maintain high-quality standards, and respond effectively to market demands.
- Investing in continuous learning and upskilling ensures long-term competitiveness and innovation.
Regulatory bodies globally are prioritizing sustainability.
95% of manufacturers believe that environmental and social governance (ESG) is a growing priority. (Source: Outlook Report: Procurement & Supply Chain, GEP, 2024)
Evolution of the Non-Durable Goods Manufacturing Industry
The non-durable goods manufacturing industry has evolved to prioritize efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability, driven by rapid advancements in technology and shifting consumer demands. Innovations in automation, real-time analytics, and sustainable materials have enabled manufacturers to respond faster to market fluctuations while reducing waste and environmental impact.
The Past
- Digital tools were rapidly adopted to ensure business continuity during lockdowns.
- Cybersecurity vulnerabilities were exposed due to accelerated remote work adoption.
- Supply chain disruptions led to investment in digital supply chain visibility tools.
- Labor shortages highlighted the need for automation and robotics adoption.
- Legacy systems posed challenges in scaling digital initiatives quickly.
The Present
- The focus on OT convergence is being increased to enhance real-time decision-making.
- Cybersecurity frameworks are being strengthened to protect interconnected systems.
- IoT solutions are being expanded for smarter inventory and production management.
- Automation with AI and machine learning (ML) are being scaled up to improve efficiency.
- Cloud adoption is being increased to support data-driven operations and scalability.
The Future
- AI-driven autonomous manufacturing systems will be extensively deployed.
- Advanced predictive analytics and digital twins will drive fully optimized operations.
- Seamless integration of edge computing will enable decentralized production control.
- Human-machine collaboration with robotics will enhance operational agility.
- Fully interconnected smart factories will use 5G and blockchain for transparency.
The future of the industry: What trends are shaping future business opportunities?
Future of the Non-Durable Goods Manufacturing Industry
Four trends are shaping the future:

Artificial IntelligenceHarness AI to revolutionize operations, optimize efficiency, and drive smarter manufacturing decisions.
AI is revolutionizing manufacturing by optimizing production, improving quality control, and enhancing demand forecasting. It enables real-time decision-making, predictive maintenance, and automation, reducing costs and improving efficiency. AI-powered insights help manufacturers respond to market changes swiftly and drive innovation for long-term growth.
Industrial Internet of ThingsConnect, monitor, and optimize production in real time with the power of industrial IoT.
IIoT enhances operational efficiency by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and seamless communication between machines and systems. It improves production visibility, reduces downtime, and enhances quality control. With cloud-based analytics, manufacturers can scale operations and achieve greater transparency and traceability.
Adaptive Supply ChainsBuild agile, resilient supply chains to navigate disruptions and meet evolving market demands.
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting strategies such as friendshoring, nearshoring, and reshoring to reduce reliance on distant, volatile regions and bring supply chains closer to stable markets or allies. Technology plays a critical role, enabling real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and automation to enhance flexibility and minimize risks. By building resilient, localized, and adaptable supply chains, businesses can better meet customer demands, control costs, and align with sustainability and transparency goals.
Regulatory ComplianceStay ahead of regulations with proactive compliance strategies and smart automation solutions.
Regulatory compliance is crucial for manufacturers to meet evolving safety, environmental, and quality standards. Digital tools such as AI and blockchain help track compliance, enhance transparency, and automate reporting. Staying compliant mitigates risks, avoids penalties, and builds consumer trust and market credibility.

Manufacturers continue to prioritize investments to keep operations running and supply chains stable
Manufacturers continue to invest in mature technologies with a focus on business continuity and to better prepare their business users for a competitive market space. Although overall tech investments have seen a recent slowdown due to high interest rates, the outlook for transformative technologies, such as AI and robotics, remains strong.
While interest in AI remains high, investments are yet to catch up.
The following chart shows the percentage of surveyed manufacturers investing in various technologies.
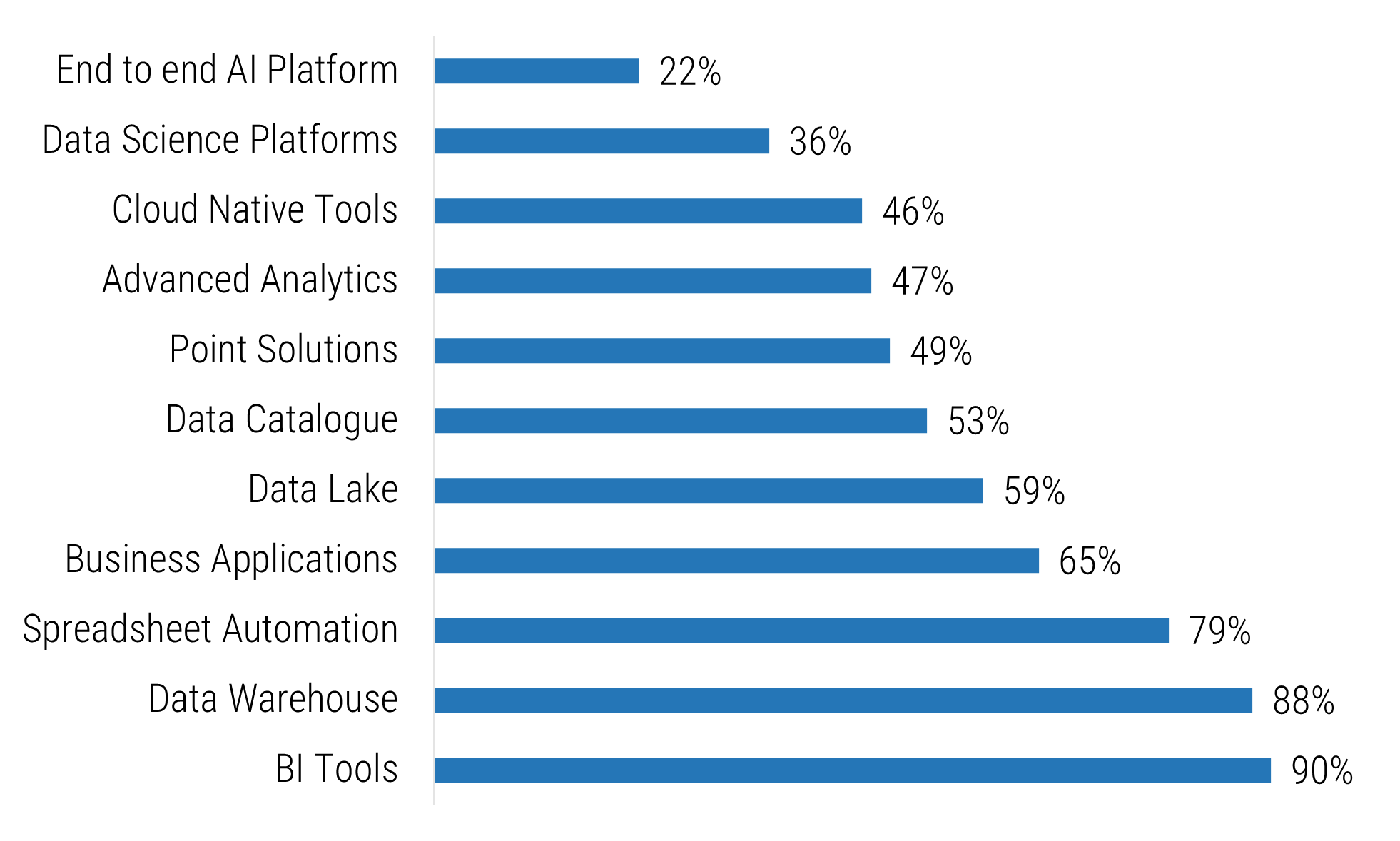 (Source: Dataiku and Databricks, 2024)
(Source: Dataiku and Databricks, 2024)
Policy will be a key driver for technology investments.
“Potential policy changes after the 2024 US elections, as well as elections across the globe, may have impacts on supply chains, demand, and long-term investment in manufacturing.
Changes to trade policy and tariffs could drive up raw material and component costs and could have ripple effects throughout the supply chain. Potential adjustments to parts of the Inflation Reduction Act could impact investment in certain aspects of clean technology manufacturing in the United States.” (Source: Deloitte, 2024)
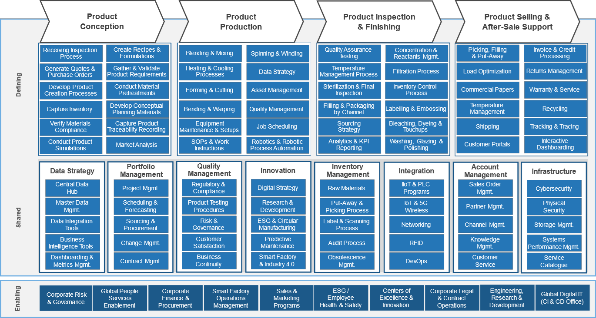
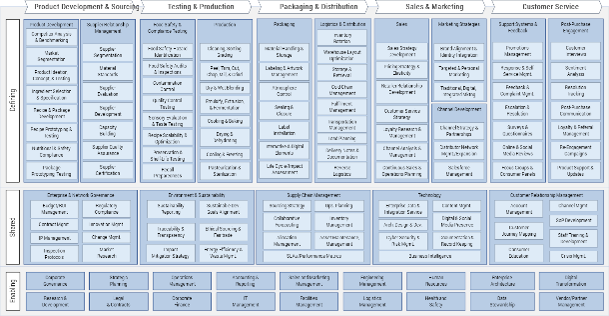
Leverage capability maps to identify cost and competitive advantages for non-durable goods manufacturing
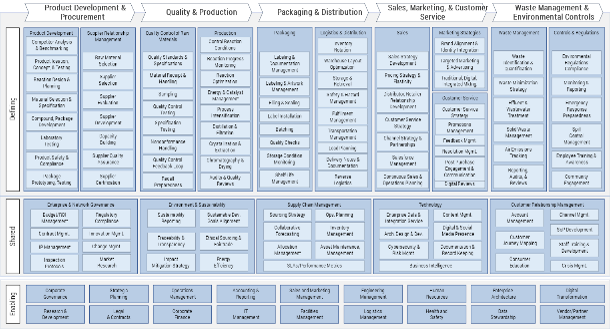
Non-Durable Goods Manufacturing
Food & Beverage Manufacturing
Chemical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
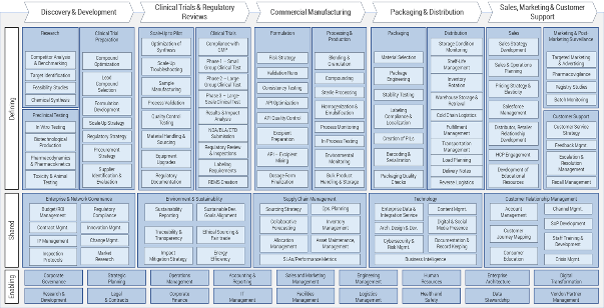
In business architecture, the primary view of an organization is known as its business capability map.
A business capability defines what a business does to enable value creation, rather than how. Business capabilities:
- Represent stable business functions.
- Are unique and independent of each other.
- Typically have a defined business outcome.
A business architecture practitioner can use this map to assess a specific area of the business.
Download the Non-Durable Goods Manufacturing Reference Architecture
Download the Food & Beverage Manufacturing Reference Architecture
Download the Chemical Manufacturing Reference Architecture
Download the Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Reference Architecture
How to use this report
Leverage this trends report to develop your digital business strategy
This trends report is intended to act as a standalone report on the non-durable goods manufacturing trends. It will help you effectively process signals in your environment and build an understanding of relevant trends, while also serving as a research-based accelerated input to the Define Your Digital Business Strategy and IT Strategy blueprints and the associated activities.
THE FUTURE OF THE NON-DURABLE GOODS MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY - TRENDS REPORT
Leverage this trends report to learn about priorities that drive measurable, top-line organizational outcomes and to unlock direct value.BUSINESS CONTEXT & IT STRATEGY
The future will bring more trends and technologies. Your organization must establish itself as the disrupter not the disrupted. You must establish a structured approach to innovation management that considers external trends and internal processes.
Artificial Intelligence
TREND 1
Harness AI to revolutionize operations, optimize efficiency, and drive smarter manufacturing decisions.
AI is transforming the manufacturing industry by enhancing efficiency, precision, and adaptability
Manufacturers are making huge commitments to AI.
Manufacturers recognize the important role of AI in the journey to Industry 4.0/5.0 maturity. AI use directly contributes to efficiency and smart operations. When working alongside machine learning, AI can perform tasks faster and more accurately than ever before.
“… more than 50 percent of top European manufacturers are currently implementing AI in some way. Germany leads, with 69 percent of manufacturers using it. In Japan that figure is 30 percent and in the United States it’s 28 percent. China brings up the rear with 11 percent.” (Source: Sandvik, 2023)
AI has an exponential impact on quality control and maintenance.
AI is very commonly used in quality control and predictive maintenance applications. AI also improves production, product development and supply chain management.
“Japanese tire manufacturer Bridgestone uses an AI tool with sensors that inspects 480 different physical items to ensure that all tires are assembled in optimal condition.” (Source: Sandvik, 2023)
Generative AI capabilities add value to the design process.
AI can follow user-instructed design goals and parameters to generate different design options. This capability is accelerating the availability of made-to-order and mass-customized products.
“One area where I think AI will be used is in made-to-order products such as tailor-made clothes, where AI can help measure the right fit for suits and shoes,” (Source: Robert Luciani, Executive Advisor at the AI Framework, Sandvik, 2023)
33% of manufacturers are looking to expand AI adoption.
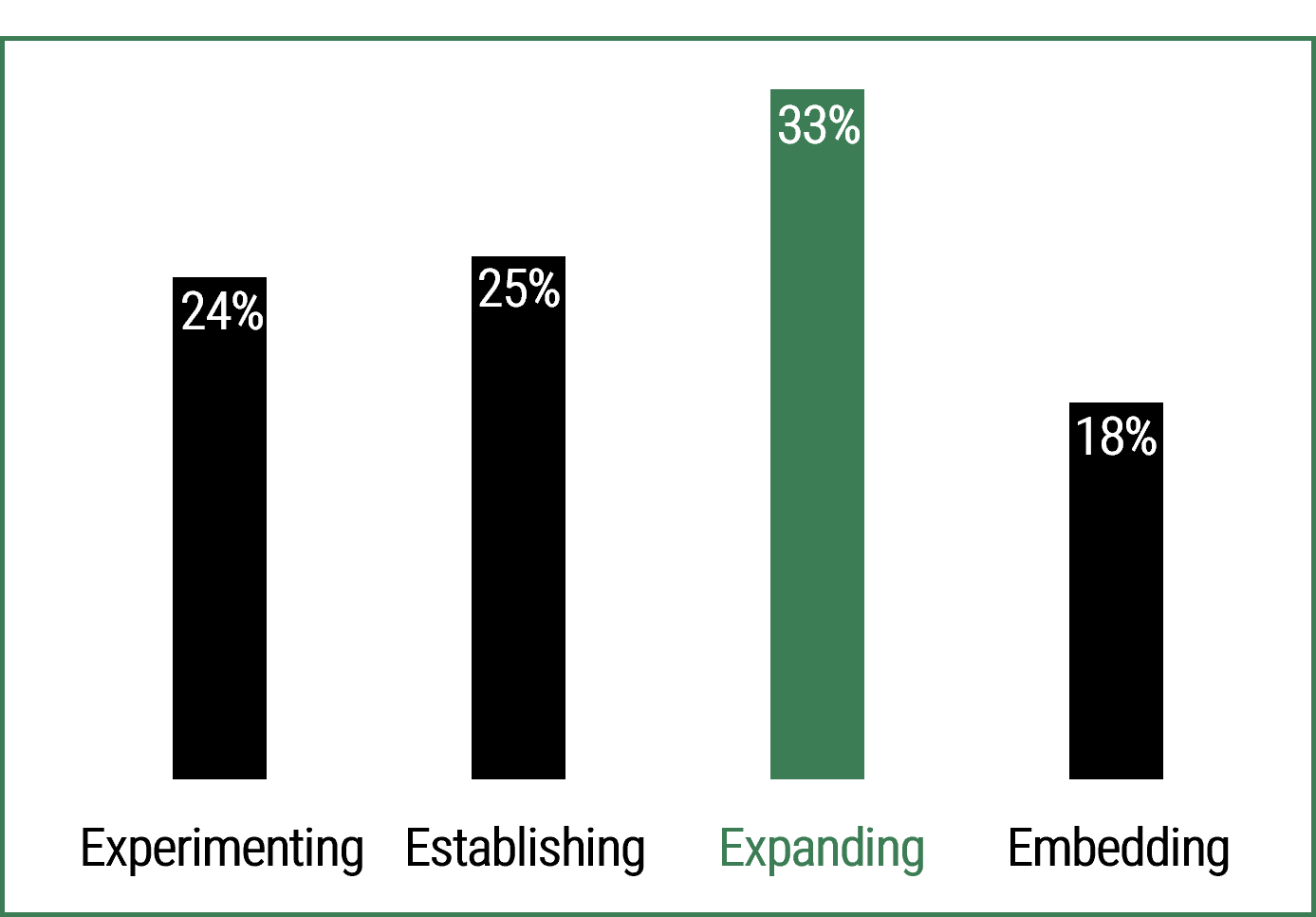
- Experimenting: Manufacturers are still exploring projects and use cases.
- Establishing: Manufacturers have a concrete business case and are beginning to execute.
- Expanding: Manufacturers are expanding AI use into multiple functions.
- Embedding: Manufacturers have several departments already using AI and are looking to embed AI capabilities into more functions. (Source: Dataiku and Databricks, 2024)
Signals
WHAT WE ARE SEEING
AI implementation is growing rapidly.
A significant number of manufacturers are integrating AI into their operations. A study by Researchscape found that 70% of manufacturers have implemented some form of AI,(Source: “Through The Roof,” Forbes, 2024) highlighting the technology's growing importance in the sector.
The AI market is exploding in value.
The AI manufacturing market is it is projected to reach US$8.57 billion by 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 44.2%. (All About AI, 2024) This expansion underscores the escalating investment and reliance on AI technologies within the industry.
AI is having an impact.
AI applications are significantly improving manufacturing processes. By reducing labor and maintenance expenses, minimizing waste, and optimizing energy consumption, AI contributes to a leaner and more cost-effective production environment.
IMPACTED CAPABILITIES
The capabilities that are listed and highlighted below receive a cost or competitive advantage through sustainability.
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
- Product Ideation, Concept & Testing
- Forecasting & Sales & Operations Planning (S&OP)
- Quality Control & Defect Detection
- Targeted & Personal Marketing
COST ADVANTAGE
- Material Handling & Storage
- Energy Optimization
- Maintenance & Asset Management
- Waste & Yield Management
Drivers
WHY YOU SHOULD CARE
There is demand for higher efficiency and productivity.
AI enhances production efficiency by optimizing processes, reducing downtime, and improving resource use. Leaders should care because this boosts profitability and operational agility.
Manufacturers are operating in an increasingly competitive environment.
AI helps manufacturers meet growing customer demands for personalized products and faster delivery. Leaders should adopt AI to stay competitive and enhance customer satisfaction.
Manufacturers struggle to address talent shortages.
AI addresses labor shortages by automating repetitive tasks and augmenting human capabilities. Leaders should invest in AI to ensure long-term operational sustainability.
Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities
- Predictive Maintenance — Manufacturers use AI technology to analyze sensor data and predict potential downtime or accidents. By forecasting equipment failures in advance, AI enables proactive maintenance scheduling to prevent disruptions. This enhances operational efficiency while reducing maintenance costs and unexpected breakdowns.
- Generative Design — Generative design leverages machine learning to replicate an engineer's approach to creating optimal designs. Using key parameters, such as materials, size, weight, strength, and cost constraints, the software generates a wide range of possible solutions.
- Quality Assurance — Quality assurance ensures that products and services consistently meet desired standards. AI-powered machine vision technology detects deviations from expected outputs by identifying visible defects. When quality falls below expectations, AI systems immediately trigger alerts, enabling swift corrective action. This proactive approach enhances efficiency and minimizes defects, ensuring high-quality end products.
 “PepsiCo’s Frito-Lay plants used AI-driven predictive maintenance to save costs and improve equipment performance. The firm could minimize unplanned downtime and increase production capacity by 4,000 hours.” (Source: AIMultiple, 2024)
“PepsiCo’s Frito-Lay plants used AI-driven predictive maintenance to save costs and improve equipment performance. The firm could minimize unplanned downtime and increase production capacity by 4,000 hours.” (Source: AIMultiple, 2024)
Challenges
- Data Quality — Poor data quality and limited access are major obstacles to AI adoption, hindering accurate insights and decision-making. Inconsistent, incomplete, or siloed data can reduce AI effectiveness and lead to unreliable outcomes.
- Business Case — The lack of robust and clear business cases is a significant barrier to AI adoption, making it difficult to justify investments and measure success. Without well-defined objectives and ROI expectations, organizations struggle to align AI initiatives with strategic goals.
- Operational Complexity — Complex infrastructure, processes, and operations pose significant challenges to AI adoption by increasing integration difficulties and operational inefficiencies. Legacy systems and fragmented workflows can hinder AI deployment and scalability.
“66% of total respondents ranked data quality and access as one of their top three barriers …” (Source: Dataiku and Databricks, 2024)
CASE STUDIES
AI is adding value for non-durable goods manufacturers
Food & BeverageAI provides predictive maintenance capabilities. (MaintainX, 2024) | Non-Durable GoodsAI detects anomalies during production. (LeewayHertz, 2024) | PharmaceuticalsAI accelerates drug discovery. (AWS, 2024) | ChemicalsAI cuts product development time. (Microsoft, 2021) | |
Challenge | SanTan Brewing struggled with reactive maintenance and lacked cost tracking per location, particularly at its pubs, which accounted for 75% of issues. Existing maintenance systems were complex and not user-friendly for field staff. | NSG Group faced difficulties detecting beading anomalies during glass production, leading to breakage, material wastage, and inefficiencies in operations. | Insilico Medicine needed scalable, flexible computing resources to accelerate its drug discovery process and reduce inefficiencies caused by manual scaling with its previous cloud provider. | Dow faced lengthy manual polyurethane-formulation processes, which took up to 18 months and required significant expertise and historical data analysis. This hindered efficiency and responsiveness to customer needs. |
Solution | MaintainX provided an easy-to-use mobile solution, enabling staff to submit work orders, track tasks, and improve overall maintenance visibility without requiring extensive training. | LeewayHertz developed an AI-powered computer vision system that detects beading anomalies in real time, providing precise alerts and enabling immediate corrective action. | By migrating to Amazon SageMaker, Insilico automated and parallelized its ML model training, enabling rapid scalability and reducing dependency on manual resource allocation. | By adopting Microsoft Azure AI and ML, Dow digitalized its formulation process, enabling the use of predictive intelligence to analyze past data, accelerate experimentation, and anticipate future product needs. |
Benefits | SanTan achieved better asset tracking, improved preventive maintenance, and reduced operational inefficiencies, completing 450 work orders in six months while enhancing team collaboration and scheduling. | The solution minimized material waste, improved operational efficiency, enhanced product quality, and enabled proactive maintenance, thus reducing downtime and optimizing resource allocation. | Insilico reduced model deployment time from 50 days to three days, improved collaboration across teams, and enhanced drug discovery capabilities, thus accelerating the development of life-saving therapeutics. | The transformation reduced formulation time from months to seconds, improved supply chain visibility, fostered greater collaboration, and positioned Dow to meet emerging customer demands proactively while enhancing sustainability efforts. |
What implication does AI use have on IT leaders and manufacturers, and their end consumers?
IT Leaders
Infrastructure Modernization
AI adoption requires upgrading legacy systems and ensuring seamless data integration across platforms. IT leaders must focus on building scalable, secure, and AI-ready infrastructures.
Data Management and Security
With AI relying on vast amounts of data, IT leaders must prioritize data governance, privacy, and compliance. Effective management ensures data accuracy, security, and ethical AI use.
Collaboration With Operations
IT teams must work closely with operations to align AI deployments with business goals. This collaboration helps bridge technical and operational needs for successful AI integration.
Manufacturers
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
AI optimizes production processes, reducing downtime and operational costs. Manufacturers can achieve higher output with lower resource consumption.
Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control
AI enables real-time monitoring to prevent equipment failures and ensure product quality. This leads to fewer defects, lower maintenance costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Agility and Innovation
AI empowers manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market demands and explore new product innovations. This agility fosters competitiveness and long-term growth.
End Consumers
Enhanced Product Quality
AI-driven quality control ensures more reliable and defect-free products. Consumers benefit from higher-quality goods that consistently meet their expectations.
Faster and Personalized Services
AI enables manufacturers to deliver customized products faster by analyzing consumer preferences. This enhances customer experience and satisfaction.
Cost-Effective Products
AI-driven efficiencies help reduce production costs, which can lead to more affordable pricing for consumers. Lower costs make advanced products more accessible to a broader audience.




