- Bulk electric providers risk penalties and grid disruption if they fail to meet NERC standards.
- Complex IT/OT ecosystems lack centralized governance, hindering consistent compliance.
- Ownership silos between control centers, substations, and corporate IT complicate controls.
- Evolving NERC requirements and adoption of hybrid systems introduce new compliance risks.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- A solid foundation enables solid security. A control framework is the first key to cost-effective compliance. It enables you to meet multiple requirements by validating one control across several obligations.
- Right-size your compliance environments. Environments are the second key to cost-effective security compliance. Environments allow you to apply a scope to your NERC CIP obligations and minimize your compliance costs.
- Understand conformance to prioritize. Conformance levels are the third key to cost-effective security compliance. Conformance levels allow your organization to make informed business decisions on how your compliance resources will be allocated.
- Ensure proactive, not reactive, audit readiness. Audit readiness is the final key to cost-effective security compliance. Take charge of your audit costs by preparing test scripts and evidence repositories in advance.
Impact and Result
- Reduces complexity and cost by aligning NERC CIP efforts under a repeatable, integrated framework.
- Enhances executive decision-making through structured compliance governance.
- Supports sustainable compliance with automated monitoring and improved control visibility.
Build a NERC CIP Compliance Program
Achieve compliance efficiently and be prepared for NERC audits.
Analyst Perspective
Efficient compliance is the best path to adaptive compliance.
Untangling the complicated landscape of compliance obligations can be challenging in any industry, but few industries couple this with the high stakes of the utilities industry. There is an ever-present need to keep your compliance efforts in lockstep with regulatory obligations, avoiding both regulatory penalties and operational risks.
A primary challenge to doing so comes from evolution, both externally as regulations are continually updated by governing bodies and internally as new technology and the convergence of IT and operational technology (OT) alter how utilities operate. With multiple catalysts for change present, maintaining a common structure for implementing and updating compliance is crucial to ensuring that your organization remains consequence-free. Moreover, it prevents the costs of your efforts from ballooning as duplicate or inefficient work is performed in silos across your organization.
Enabling informed and effective compliance decisions starts from having a uniform understanding of your obligations and implementing standardized controls that provide coverage, not just comprehensively but also efficiently. In doing so, you prepare your organization to meet its obligations today and to be agile enough to incorporate the needs of tomorrow seamlessly.

Evan Garland
Research Analyst, Industry Practice
Info-Tech Research Group
Your Challenge
Your Challenge
- Bulk electric providers in North America must comply with North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) standards or face penalties, including significant fines and reputational damage, as well as risks to the grid system itself and its many dependencies.
- Many utilities operate complex IT/OT environments that lack centralized governance, making it difficult to implement and sustain effective compliance across physical substations, control centers, and corporate systems. This is exacerbated when ownership and operations differ, necessitating specific measures.
- As utilities adopt smart grid or hybrid IT systems, they face new cyber and compliance risks that demand ongoing adaptation, in addition to evolving NERC requirements.
Common Obstacles
- Siloed IT and OT teams result in inconsistent security practices, unclear ownership of controls, and fragmented incident response processes. Similar issues arise when organizations attempt to converge IT and OT processes or personnel without proper compliance oversight.
- Legacy infrastructure and proprietary operational systems can bring compliance "baggage" in the form of unique controls or methods that complicate efforts to implement common or modern frameworks and structure.
- Constraints in staffing, funding, and cyber expertise limit the ability to monitor control efficacy, maintain audit readiness, adapt to evolving standards, and respond to NERC audit findings in a timely manner.
Info-Tech's Approach
- Use a best-of-breed security framework to provide coverage of major information security requirements, while still maintaining the ability to adapt to evolving needs.
- Provide senior management with a structured framework for making business decisions on allocating costs and efforts related to cybersecurity and data-protection compliance obligations.
- Enable long-term compliance by promoting sustained monitoring, automated reporting, and clear guidance for integrating NERC Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) policies into your IT and OT environments.
Info-Tech Insight
- A control framework is the first key to cost-effective compliance. It enables you to meet multiple requirements by validating one control across several obligations.
Your Challenge
The complexity – and potential cost – of compliance with standards is increasing.
- Compliance has high stakes and is highly scrutinized. NERC CIP violations can lead to financial penalties of up to US$1 million per day, per violation. Beyond the fines, noncompliance exposes utilities to increased audit frequency, reputational damage, mandatory mitigation plans, and potential legal liability — especially when failure to meet obligations results in cybersecurity incidents that affect the Bulk Electric System (BES).
- IT/OT environments are sprawling and hard to govern. Utilities operate across a patchwork of substations, control centers, corporate systems, and other vendor-managed assets. These assets often fall under different ownerships, control models, and technologies, making it difficult to apply standardized compliance measures and ensure consistent security controls.
- Modernization introduces fast-moving and distributed risks. As utilities adopt smart grid technologies, cloud-based platforms, and IoT-connected devices, their cyber-physical infrastructure grows more exposed. Many organizations are underprepared to align evolving architectures with static or legacy compliance programs, especially as NERC updates introduce new obligations.
Common Obstacles
Utilities face persistent barriers to achieving and sustaining NERC CIP compliance.
IT/OT environments complicate governance.
Utilities often operate with siloed IT and OT systems, leading to inconsistent security practices and unclear ownership of controls. This fragmentation hampers the implementation of standardized compliance measures across diverse assets and access points.
Legacy infrastructure limits security measures.
A significant portion of utility infrastructure consists of outdated systems that are challenging to secure, patch, and monitor. These legacy systems often lack compatibility with modern compliance tools, increasing their vulnerability to cyberthreats.
Resource constraints hinder current and evolving compliance efforts.
Utilities frequently encounter shortages in skilled personnel and funding dedicated to cybersecurity. These shortages impede their ability to maintain continuous audit readiness and respond effectively to NERC audit findings. As well, periodic updates to NERC CIP standards requires utilities to adapt their compliance strategies continuously, which creates a steady stream of work for compliance efforts to accommodate.
There are more points of vulnerability than ever before. According to NERC, the number of susceptible points on US electrical networks increased by 60 per day in 2023.
Source: "US electric grid growing more vulnerable," Reuters, 2024
Direct threats from bad actors are on the rise. US utilities faced a near 70% jump in cyberattacks in 2024 over the same period in 2023.
Source: "Cyberattacks on US utilities surged," Reuters, 2024
Info-Tech's Approach
Make NERC CIP compliance sustainable, visible, and integrated across IT and OT.
- Structured frameworks aligned to NERC CIP standards: Info-Tech's analysts guide utilities through the development of a robust, repeatable NERC CIP compliance management program. This structured framework aligns with standards such as CIP-003 through CIP-013 and helps simplify governance across both traditional IT environments and operational environments. It promotes consistency across substations, control centers, corporate offices, and third-party service relationships.
- Support for cross-domain environments: Whether a utility is operating legacy
on-premise systems or adopting hybrid/cloud-based architectures, our guidance addresses configuration gaps, access control fragmentation, and inconsistent evidence documentation. We help bridge IT/OT silos to improve oversight and ensure that compliance controls adapt to the unique realities of operational assets. - Long-term compliance enabled through monitoring and automation: Making continued use of our compliance management tool ensures that compliance is not a reactive checkbox exercise but a proactive and adaptive process.
Build and operationalize a NERC CIP compliance framework
NERC CIP compliance requires more than documentation – it requires structure, strategy, and sustainable execution.
Your Challenge
Both compliance and non-compliance costs are high. NERC CIP violations can trigger severe regulatory fines, increased audit scrutiny and reputational damage, even before accounting for the significant costs of a security breach. But it is also expensive to cover all compliance obligations, especially across multiple sets of regulations
and standards.
Complex IT/OT environments challenge governance. Utilities operate across a fragmented mix of substations, control centers, cloud platforms, and vendors. Different ownerships and controls make it difficult to apply compliance measures consistently across the enterprise.
Common Obstacles
Both IT/OT siloing and convergence create challenges. Silos cause duplicate efforts and policy drift, while convergence requires clear ownership and attention to new risks.
Legacy systems are often incompatible with modern security tools or patching practices, creating vulnerabilities that are difficult to address within a CIP-compliant framework.
Limited staffing and funding reduce the ability of utilities to monitor controls, track regulation changes, and meet audit demands.
Info-Tech's Approach
Build a structured framework aligned to NERC CIP requirements to ensure consistent governance, clear role accountability, and unified compliance practices across IT and OT environments.
Standardize controls, evidence collection, and documentation procedures to streamline audit readiness and reduce the complexity of maintaining compliance across legacy and modern systems.
Embed automated monitoring and continuous reporting into daily operations to proactively detect compliance drift, improve visibility, and sustain long-term alignment with evolving CIP standards.
Insight Summary
A solid foundation enables solid security.
A control framework is the first key to cost-effective compliance. It enables you to meet multiple requirements by validating one control across several obligations.
Right-size your compliance environments.
Environments are the second key to cost-effective security compliance.
Environments allow you to apply a scope to your NERC CIP obligations and minimize your compliance costs.
Understand conformance to prioritize.
Conformance levels are the third key to cost-effective security compliance.
Conformance levels allow your organization to make informed business decisions on how your compliance resources will be allocated.
Ensure proactive, not reactive, audit readiness.
Audit readiness is the final key to cost-effective security compliance.
Take charge of your audit costs by preparing test scripts and evidence repositories in advance.
Understand the consequences of risk and act accordingly.
Compliance risk in NERC CIP refers to financial penalties and operational mandates to achieve missed compliance requirements. Security risk involves cyberthreats, data breaches, and, in the worst cases, loss of grid functionality. Meeting NERC CIP requirements is not only necessary to remove regulatory risk, but it is also one of many components that will ensure your operations remain secure and your service remains uninterrupted to those who depend on it.
Project Benefits
IT Benefits |
Organizational Benefits |
|---|---|
|
|
Case Study
How did one of the largest publicly owned utilities in the United States automate NERC CIP compliance?
INDUSTRY: Public Electric Utility
SOURCE: Parsons/SigmaFlow Vendor Case Study
Challenge
One of the largest publicly owned electric utilities in the US encountered inefficient, inconsistent compliance processes while trying to meet CIP obligations. The CIP compliance team struggled with manual, ad hoc methods – subject matter experts (SMEs) used disparate templates and spreadsheets to track required tasks and evidence. This led to inconsistent data and labor-intensive monitoring.
Without a centralized view of compliance activities, it was hard to gauge readiness or identify gaps in a timely manner. The team made significant efforts chasing updates and sending reminders, rather than improving the quality of compliance evidence. Facing ever-growing regulatory requirements, the utility recognized that the status quo was unsustainable and sought a more efficient, automated solution.
Solution
The utility adopted the SigmaFlow compliance management platform, which provided a comprehensive system for workflow management and evidence tracking. This enabled the utility to replace its manual processes with an integrated digital framework.
Key features of the implementation included automated workflows for recurring tasks, standardized protocols for evidence recording, and dashboards for real-time visibility into the current state of compliance posture.
Although, during the rollout, some departments were initially wary of losing the "freedom" to use their own templates, they soon appreciated the structure of the platform.
Results
Implementing the vendor's platform yielded significant improvements in audit readiness and efficiency. The utility now maintains a continuous state of CIP audit preparedness. Notably, the most recent NERC CIP audit team praised the utility's high level of automation in managing compliance.
This implementation demonstrates how a targeted compliance initiative can drive measurable improvements to the efficiency and maturity of a utility's regulatory compliance program, turning a manual and reactive process into a proactive and streamlined operation.
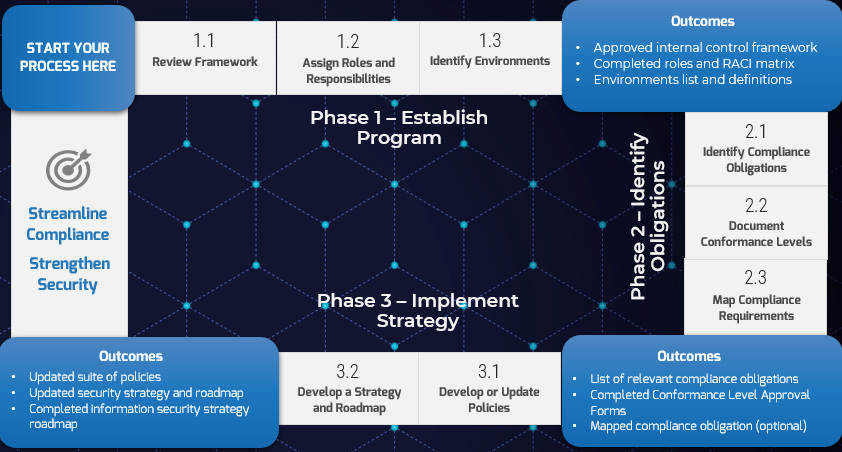
Info-Tech's Methodology to Improve NERC CIP Compliance
1. Establish Program |
2. Identify Obligations |
3. Implement Strategy |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Phase Steps |
1.1 Review framework. |
2.1 Identify compliance obligations. |
3.1 Develop or update policies. |
Phase Outcomes |
|
|
|
Is this research right for you?
Should you use a GRC or an Excel tool?
This research product offers Excel-based tools to help organizations manage their security compliance obligations.
Excel spreadsheets are an excellent way to manage compliance data, up to a point.
Organizations that have more complex structures and greater numbers of compliance requirements should consider the use of a special governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) tool.
Even if these organizations opt to use a GRC tool rather than the Excel tools provided, this research product may still help them establish their security compliance program.
Operational Environments
Organizations with more than five separate operational environments should consider a GRC tool.
Compliance Obligations
Organizations with more than ten security and privacy/data protection compliance obligations should consider a GRC tool.
Blueprint Deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals.
Security Compliance Process Template

The Security Compliance Process Template is a structured template that will help your organization establish, implement, and track security compliance to meet policy and business needs.
Key Deliverable
NERC CIP Compliance Management Tool
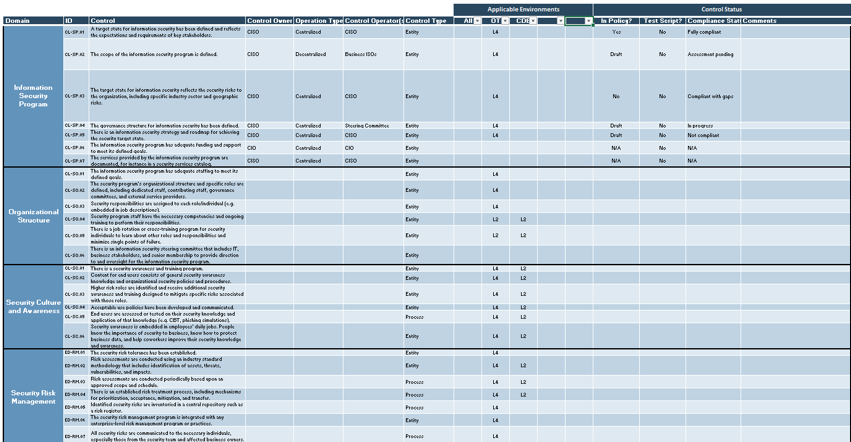
The NERC CIP Compliance Management Tool is a compact GRC system in a convenient spreadsheet. It will guide you through the process of consolidating your compliance environments and obligations and tracking your control implementation progress.
Measure the value of this project
Consider tracking the following metrics to measure the value of your compliance management program.
Metric |
Expected Improvement |
|---|---|
Number of gaming controls required for compliance obligations |
The use of a control framework may reduce the number of controls by 25% to 50%. |
Control implementation costs |
The use of conformance levels may reduce implementation costs by 25% per control, |
Control maintenance costs |
The use of environments to scope control requirements may reduce maintenance costs by 25% to 50%. |
Audit costs |
Test scripts and evidence preparation may reduce audit costs by up to 50%. |
Compliance management efforts |
The efforts required for overall compliance management may be reduced by 25% |
When properly implemented, a good compliance program is efficient, cost-effective and adaptable.
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit
"Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful."
Guided Implementation
"Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track."
Workshop
"We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place."
Consulting
"Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project."
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks are used throughout all four options.
Guided Implementation
What does a typical GI on this topic look like?
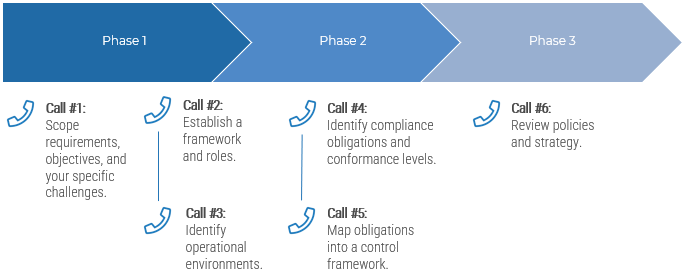
A Guided Implementation (GI) is series of calls with an Info-Tech analyst to help implement our best practices in your organization.
A typical GI is between six to ten calls over the course of two to four months.
Workshop Overview
Contact your account representative for more information.
workshops@infotech.com 1-888-670-8889
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 |
|
Activities |
Establish Program |
Identify Obligations |
Implement Strategy |
Next Steps and |
1.1 Review framework. |
2.1 Identify compliance obligations. |
3.1 Develop or update policies. |
4.1 Complete in-progress deliverables. |
|
Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
Phase 1
Establish NERC CIP Compliance Program
Phase 1 |
Phase 2 |
Phase 3 |
|---|---|---|
1.1 Review framework. 1.2 Assign roles and responsibilities. 1.3 Identify environments. |
2.1 Identify compliance obligations. 2.2 Document conformance levels. 2.3 Map compliance requirements. |
3.1 Develop or update policies. 3.2 Develop a strategy and roadmap. |
This phase will walk you through the following activities:
- Reviewing and adopting a NERC CIP control framework
- Understanding and establishing roles and responsibilities for NERC CIP compliance management
- Identifying and scoping operational environments for applicable compliance obligations
Build a NERC CIP Compliance Program
Enforce NERC CIP standards with purpose
What is NERC CIP?
The NERC CIP standards are a set of mandatory cybersecurity requirements that safeguard the BES across North America. These standards help electric utilities protect against cyberthreats and maintain grid stability. NERC CIP governs systems and assets that impact:
- Transmission substations, control centers, and generation control systems.
- Physical and cyber access to BES Cyber Systems.
- Vendor interactions and third-party risks.
- Patch management, system baselining, incident response, and recovery procedures.
NERC CIP Compliance: What is the role of utility and IT/OT leaders?
NERC CIP compliance is mandatory for any utility that operates assets connected to the Bulk Electric System (BES). This means that:
- Electric utilities must implement the current iteration of all applicable CIP standards (e.g. CIP-002 through CIP-014) and maintain audit readiness.
- IT and OT leaders must coordinate to ensure consistent application of controls across physical substations, cyber assets, and hybrid cloud environments.
NERC CIP: Key Requirements
There are 13 CIP standards that are currently subject to enforcement. Among the more critical mandates are the following:
- Access Control and Personnel Training
(CIP-004 / CIP-006)- Utilities must limit access to authorized personnel, following the principle of least privilege. Physical access controls are required at critical facilities.
- Background checks and annual cyber-awareness training (in an organized program) are mandatory.
- Configuration Management and Patch Updates (CIP-007/CIP-010)
- All BES Cyber Systems must follow secure configuration baselines and receive timely patch assessments.
- Unauthorized changes must be detected and logged using change detection tools.
- Incident Response and Recovery (CIP-008/
CIP-009)- Formal incident response plans must be in place and regularly tested.
- Utilities must track reportable incidents and have recovery procedures to restore BES operations following a cyber event.
Operationalize compliance to safeguard public safety and autonomy
Why is NERC CIP compliance critical for electric utilities?
Electric utilities operate the foundational infrastructure that powers homes, hospitals, industries, and emergency services. NERC CIP standards are legally binding regulations, designed to secure this infrastructure from both physical threats and cyberthreats. Non-compliance not only invites steep penalties but also exposes utilities to significant operational, financial, and reputational risks. As grid modernization and IT-OT convergence introduces greater operational complexity and cyberthreats become increasingly prevalent, embedding compliance into daily operations is essential for resilience, audit success, and public safety.
Operational Risks and Public Safety: The Security Risks That Stem From Noncompliance
Failure to implement required NERC CIP controls — such as access restrictions, patch management, and incident response — leaves utilities vulnerable to cyberattacks and sabotage. These gaps can be exploited to cause outages, disrupt power distribution, or disable critical assets.
A single compromised substation or control center could cascade across the grid, affecting millions and disrupting essential services such as hospitals, water treatment plants, and emergency communications.
Loss of Autonomy and Audit Readiness Business Risk
Repeated compliance failures trigger heightened oversight from regulatory bodies, reducing a utility's autonomy and increasing administrative burden.
Inconsistent audit preparation, missing evidence, or poorly defined roles can erode trust and lead to fines, mandatory mitigation plans, or deferred investment in innovation. Compliance lapses can also delay critical projects and increase risk during mergers, acquisitions, or rate filings.
